Back to api.video Glossary
Gamma correction

What is gamma correction?
Definition: Gamma correction is a crucial nonlinear operation in digital imaging and video processing that adjusts the luminance (brightness) of images or video content. It consists of two main processes: gamma encoding and gamma decoding. This technique optimizes how brightness is represented in digital media and displayed on screens, accounting for differences between how cameras capture light and how human eyes perceive it.
Key Aspects:
Purpose:
- Ensures accurate brightness representation on digital displays
- Optimizes data storage and transmission by focusing on perceptually important information
Human vs. Camera Vision:
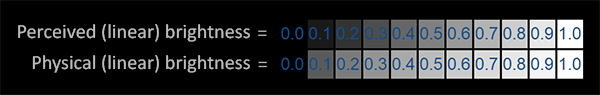
- Cameras have a linear response to light intensity
- Human vision has a nonlinear response, more sensitive to changes in darker areas
- Gamma correction bridges this gap, making digital images appear more natural to human eyes
Encoding Process:
- Redistributes tonal information to match human perception
- Allocates more data to shadow details and less to highlights
- Compensates for the overemphasis on brightness in camera sensors
Decoding Process:
- Adjusts stored digital information for proper display on various screens
- Accounts for different display technologies and their characteristics
Practical Applications:
- Improves overall image quality and detail visibility
- Ensures consistent appearance across different devices and displays
- Essential for accurate color reproduction in digital media
Considerations:
- Different displays may interpret gamma values differently
- Requires careful balancing to preserve important visual information while optimizing data usage
Gamma correction is fundamental in digital imaging, ensuring that what we see on our screens closely matches our natural visual perception, despite the limitations of both capture and display technologies.

